
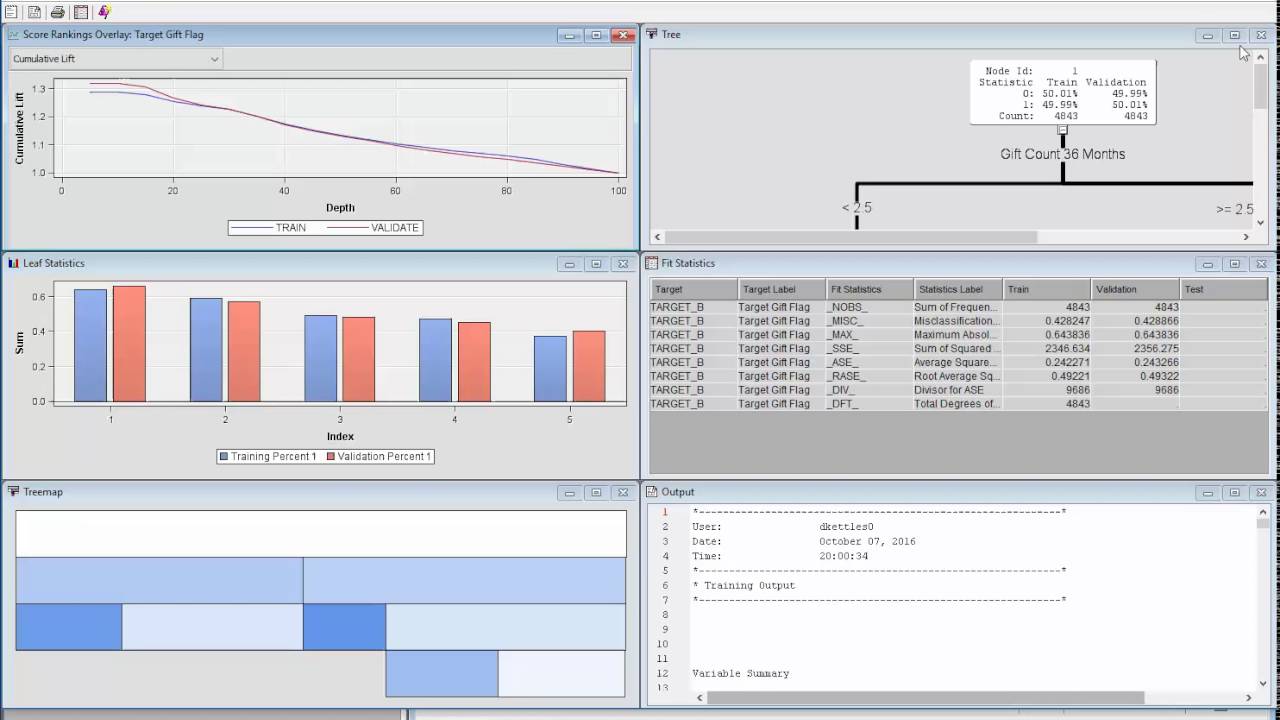
Sas segmentation violation in task program code#
This code enables you to obtain the same results from running in SAS 9.4 when running the DATA step in CAS. Listing _ROWID_ as the last variable in the BY statement creates a unique BY group for each row. Proc print data=casuser.cascars (obs= 10 ) * Sorting the data is not required when you run in CAS. Adding this option creates the sequential _ROWID_ variable that I can then use in the BY statement:Ĭaslib _all_ assign /* Creates the CASUSER libref.
This is the same code I ran earlier in CAS, but this time, I used the ADDROWID option when creating the CARS table.
Sas segmentation violation in task program how to#
Here is an example of how to use ADDROWID and _ROWID_ to maintain the order of the data. Example Using ADDROWID and _ROWID_ in CAS logic with ADDROWID to generate the same results in CAS that you get in SAS 9.4. So you can perform BY-group processing using FIRST. The value of _ROWID_ is 1 for the first row, 2 for the second, 3 for the third, and so on. This option creates the new variable _ROWID_ that increments numerically for each row in the table.
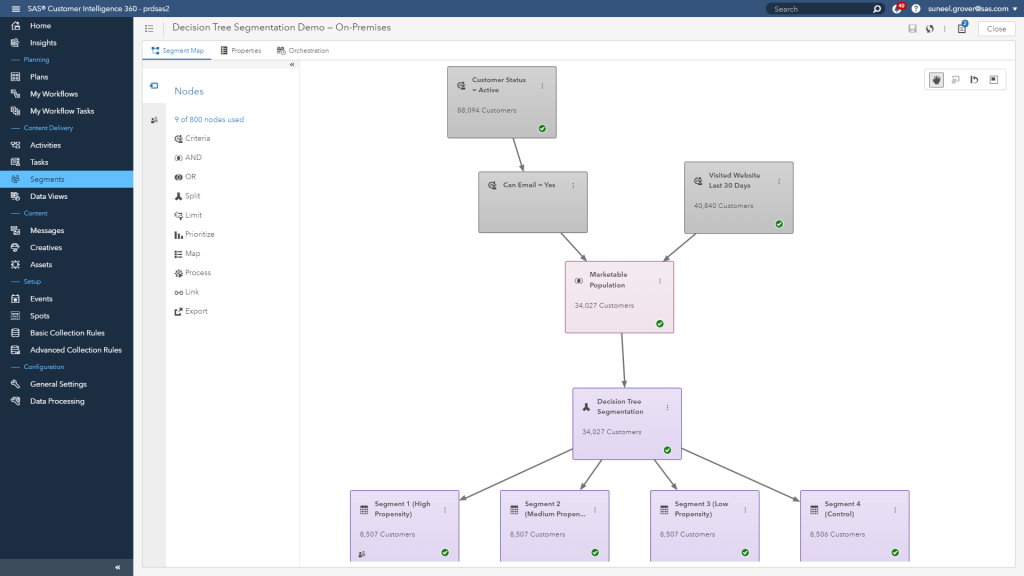
The ADDROWID data set option was created so that the results created in SAS can be replicated when running in CAS. When processing in CAS, the BY groups are retained, but the order of rows within the BY group cannot be guaranteed. However, the value of model is not the same each time I run the step in CAS. This output is the same each time I run this code in SAS 9.4. The output from running the step in SAS 9.4 shows the make in alphabetic order with the first model based on an alphabetic sort order, which is the original order of the data. The model that is associated with the make is different in the output that is created in CAS. Here is the output from both PRINT procedures, which are clearly not the same. I compare the output of running a DATA step using BY-group processing in SAS 9.4 to the output produced from running the exact same code in CAS. In this example, I use the SASHELP.CARS data set. Here is an example of how the order of the data can be different when running a DATA step in CAS. Since the order is not guaranteed when running in CAS, results are almost assuredly different when you compare the output from running in SAS 9.4 to running in CAS. This reordering becomes very important when you use FIRST. This change in order can occur with or without a BY statement. However, because of the process by which CAS distributes and reassembles the data, the order of the data within each by group is not guaranteed. Each resulting BY group is maintained when distributing the code and data. When you use a BY statement in the DATA step that is running in CAS, the data is grouped by the unique values of the BY variable. CAS DATA step processing with a BY Statement


The code that executes on each worker and thread is the same, but the portion of data is unique for that worker and thread. Source: SAS Help Center: Data Step Processing in CAS When a DATA step runs in CAS, CAS distributes the code and data across multiple workers and threads, as shown below: It is essential to understand how processing works when running a DATA step in CAS to avoid possible unexpected results. However, running a DATA step in CAS is different. In SAS 9.4, the order of your data remains constant when you run a DATA step with or without a BY statement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
